Microdiscectomy
Gold Standard Slipped Disc Surgery
Physiotherapy
Spinal Injections
Microdiscectomy
Lumbar Laminectomy
Spinal Fusion Surgery
Lumbar Interbody Fusion
Anterior Cervical Fusion Surgery
Posterior Cervical Spine Surgery
Disc Replacement Surgery
Kyphoplasty/ Vertebroplasty
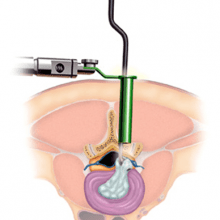
Microdiscectomy is a minimally invasive spine surgery procedure. It is Gold Standard surgery for removal of lumbar disc herniation and is one of the most commonly done spine surgery. In this surgery, herniated part of the disc, which is compressing spinal cord, is removed with the help of microscope and special retractors (e.g. tubes). A very small hole is made on the skin. Microdiscectomy surgery is very safe with predictable results.
Microdiscectomy Indications:
Microdiscectomy surgery is required when MRI shows disc herniation in lumbar spine and patient has severe leg pain. We follow following principles to decide about the surgery:
- Severity of pain: Pain should be severe enough to affect patient’s day to day life. Surgery for minor pain is not recommended and patient should try other methods of treatment.
- Duration: Pain should be of long duration. A pain of recent onset might get better with medical treatment (medicines, physiotherapy, epidural injection).
- Response to medical treatment: It is recommended to always start with medical treatment. If patient doesn’t get relief, epidural injection can be tried. Majority of the patients get better by these treatments and don’t need surgery.
- Pathology: A matching pathology should be seen on MRI/ CT explaining patient’s symptoms. Only when there is a pathology explaining patient’s symptoms, a surgery to treat that pathology will help alleviate patient’s symptoms, which is the aim of the microdiscectomy surgery.
There are situation when these steps are not followed and microdiscectomy is recommended right-away.
- Cauda Equina Syndrome: When there is a large piece of herniated disc compressing the spinal cord and patient has loss of bowel-bladder control, loss of sensation and weakness in legs, it is advisable to remove herniated disc on emergency basis.
- Severe Unbearable Pain: Severe pain, which is not tolerable and doesn’t let patient perform routine day to day activities, requires immediate surgery.
Advantages of Microdiscectomy:
Microdiscectomy offers all advantages of minimally invasive spine surgery:
- Very safe,
- Immediate and predictable results, Microdiscectomy using a tube
- Very small skin incision,
- No/ minimal blood loss,
- No/ minimal complications,
- Minimal post-operative pain,
- Minimal need of medications after surgery,
- Day care/ one day hospital stay,
- Immediate mobilization (within few hours after the surgery),
- Quick recovery and return to routine activities.
Complications of Microdiscectomy:
Microdiscectomy has great safety profile with minimal risk of any complication. Even routine complications, e.g. pain and infection, are extremely rare. There is about 2% chances of recurrent disc herniation at the same operated level. Some patients can have dural tear (the thin layer covering spinal cord). This leads to CSF (Cerebro-Spinal Fluid) leak which requires special attention during recovery period. Also, as only the herniated part of the disc is removed, and rest of the degenerated disc is still lying in inter-vertebral space, it may degenerate further, especially with heavy activities and can cause disc degeneration (Lumbar Spondylosis) related symptoms, i.e. backpain, recurrent disc herniation, spinal stenosis.
Recovery after Microdiscectomy:
Patients can be mobilized within few hours after the surgery. They can be discharged from the hospital on the same day or next morning. Routinely, physiotherapy is not required after the surgery. However, patients who had leg muscle weakness before surgery, might require a short course of physiotherapy after the surgery. It is recommended to avoid heavy lifting, sitting on floor, sitting for long time, driving for long duration for 4-6 weeks to prevent recurrence of disc herniation.
An office going person can resume his duties within 2-3 days after the procedure. Patients who have heavy manual labour activities requires 4-6 weeks break before joining work. Sports activities are usually allowed after 3-6 months.
Alternatives to Microdiscectomy:
Laminectomy (Lumbar decompression): A procedure involving slightly bigger skin incision and removal of more bone can be done. Many surgeons are more familiar with this traditional technique than microdiscectomy. Recovery is still fairly quick.
Endoscopic Discectomy: An endoscope is inserted inside the target disc and herniated part of the disc is removed. This procedure can be done under local anaesthesia also as day care procedure.
LASER Disc Decompression: A LASER probe is inserted in the herniated disc. Emitted LASER rays coagulate/ liquify nearby disc material. This leads to reduction of disc pressure on spinal nerves and neutralization of disc tissue which creates inflammation around the spinal nerves.