Best Spine Surgeon in Mumbai | Dr. Amit Sharma

+91-9967600461
draks777@gmail.com
Osteoporosis: Know all about it!
Osteoporosis: Know all about it!
Spine Osteoporosis Treatment
Osteoporosis is a bone disease in which basic framework of bone is weakened. There is associated lack of calcium in the bone. This leads to fragile bones which are prone to fractures. Osteoporosis primarily affect old patients; however, in certain disease process it can affect young individuals also. These patients are prone to develop fractures of spine, hip, wrist and other bones.
Risk factors for Osteoporosis:
- Old age,
- Female gender,
- Inactivity (sedentary lifestyle) and Lack of exercises,
- Rheumatological disorders,
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption,
- Kidney diseases, blood cancers (Multiple Myeloma, Leukemia etc.),
- Lack of Vitamin D and calcium in diet,
- Lack of exposure to sunlight,
- Family history of osteoporosis (genetic),
- Long term use of certain medications (steroid, anti-epileptics),
- Lack of sex hormones (estrogen in females, testosterone in males).
Symptoms:
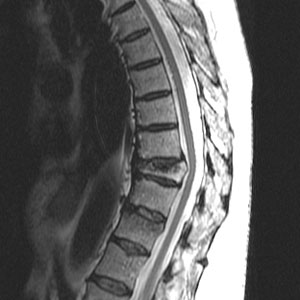
Majority of the patients present with insufficiency fracture of bones. Many patients might have chronic pain in different parts of the body secondary to microscopic/ hairline fractures of spinal vertebrae and other bones. Pain is more on weight bearing (sitting, standing, walking) and gets better with rest. There may be associated spine deformity due to bone collapse. If part of fractured vertebra projects significantly in spinal canal, it can compress on spinal cord and can lead to symptoms of spinal stenosis.
Prevention of Osteoporosis:
We cannot change non-modifiable risk factors (age, gender, genetics etc.). However, modifiable risk factors should be taken care to prevent, cure and halt the progression of osteoporosis.
- Exercise and lifestyle changes: Living an active life style and regular exercises will make bones stronger. Weight bearing exercises will strengthen basic framework of bone. Exercises will also lead to better muscle strength which prevent loss of balance and fall.
- Adequate Calcium and Vitamin D intake: Our diet is usually not sufficient to supply daily requirement of calcium and vit. D. Supplemental doses of calcium and vit. D should be taken by high risk individuals. Also, an exposure to early morning sunlight will help body to develop vit. D. Vit. D supplementation are very important in patients suffering from kidney diseases. Foods with high calcium contents, e.g. dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), dark green leafy vegetables (broccoli, spinach etc.), tofu, foods fortifies with calcium (fruit juices, breads) should be consumed more often.
- Smoking and Alcohol: Even if a complete abstinence is not possible, cutting down on amount of smoking and alcohol will reduce harmful effects.
- Medications: Some medicines cause/ worsen osteoporosis as side effect. Please speak to your doctor if a modification in your existing medication is possible to change them to ones which do not cause osteoporosis.
Prevention of fall:
Elderly patients are prone to fall due to poor muscle strength, loss of balance, impaired vision, certain medications (sedatives/ antidepressants) and mental-physical dysfunction. Fall may lead to fractures in these old patients having osteoporosis. Certain modifications in surroundings can be done to prevent fall.
- Use of cane/ walker/ wheel-chair.
- Wearing shoes with non-slippery soles.
- Using shoes/ sandals that grip the feet.
- Walking on non-slippery surfaces.
- Taking help of others.
- Keeping floor free of clutter.
- Having rough floor in bathroom.
- Having side rails, side-bars to hold on to while walking.
- Keeping stairs well-lit and having handrails on both sides.
- Avoiding carpets and rugs.
- Using rubber mat on slippery surfaces/ bathroom.
- Keeping flashlight handy.
Complications of osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis causes weak and brittle bone which are prone to fracture. Elderly with poor walking balance tend to fall which leads to fracture of the spine, hip, wrist and other bones. Some-times even a trivial trauma of day to day activity is sufficient to cause these fractures, especially in spine. Osteoporosis makes treating these fractures very difficult as weak bones do not hold on to orthopedic metal implants strongly and they heal slowly. This causes various complications in the recovery phase, such as need of long bed rest, implant failure (screw-plate loosening and breakage), bed sores, lung and urine infection etc., causing severe disability and dependence. Minor hairline fractures in vertebra and other bones can cause chronic pain. Hence it is very important to detect and treat osteoporosis in early stages.
Diagnosis of Osteoporosis:
Ideally, osteoporosis detection should be a part of routine health check-up. Most of the times, osteoporosis is diagnosed when an elderly presents with a broken bone. Osteoporosis should be suspected in every individual who presents with a broken bone in old age. Following tests are used to diagnose osteoporosis:
- X-ray: As x-ray is cheap and easily available, it is usually done as first line of investigation. Also, x-ray is required to detect bone fractures. An osteoporotic bone will show lack of calcium on x-ray.
- DEXA Scan: DEXA (Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) is gold standard test to detect osteoporosis. A DEXA scan is useful as it will quantify osteoporosis , which will help in
- Classifying the grade of osteoporosis,
- Predicting risk of developing fracture,
- Assessing the need of treatment,
- Assessing response to treatment.
- MRI/ CT Scan: A specialised scan might be required to assess underlying spinal structure (MRI) or bone details (CT). A CT scan can also help in grading osteoporosis.
- Blood tests: Certain blood tests might be required to rule out underlying/ associated medical problems (e.g. Blood value of calcium and vit. D, Rheumatology tests, Cancer markers, Kidney profile, hormonal assay, markers of bone regeneration etc.)
- Other tests to detect an underlying/ associated disease. E.g. bone biopsy for tumors, ultrasound examination to assess kidneys etc.
Treatment of Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis is a medical disease. However, it is very difficult and tedious process to treat osteoporosis. Prevention is better than cure holds true here. Following medical treatments are advised:
- All the measures described in prevention section should be utilized. Better and nutrition, active lifestyle, regular exercises, and moderate weight bearing will help strengthen the bones.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Correct doses keeping patient’s age, weight and requirement in mind are prescribed by your doctor. It is not advisable to treat yourself and take these as health supplement only when treating osteoporosis. Vitamin D helps in calcium resorption from intestine and helps it’s deposition in the bone.
- Osteoporosis Medications: Specific medications are given to help bone recover it’s strength.
- Calcitonin Nasal Spray: Primary function of this medicine is to reduce pain associated with osteoporotic fracture. They also reduce calcium washout from the bone.
- Bis-phosphonates: These medicines prevent calcium washout from the bones in the blood. They are available in different dosing schedules (weekly, monthly, yearly) in oral and injectable forms.
- Teriparatide: This group of medicines increases the basic framework of the bone and provide additional site for bone deposition. They are given as subcutaneous injection (like insulin) and have to be taken on daily basis for a long duration (ideally 2 years).
- Denosumab: Inhibits bone eating cells and prevent bone degradation leading to progression of the disease.
- Hormonal Supplements: Sex hormone supplements are given, especially to females, as they are more prone to develop osteoporosis.
Usually a combination of these treatments is given. In addition, if there is fracture of spine/ hip/ wrist, it is treated as per the recommendation by surgery or casting/ bracing.
Osteoporosis, characterized by weakening bone structures and reduced calcium content, presents a significant challenge for many, especially the elderly. It’s not just about brittle bones; the ripple effects of spinal, hip, and wrist fractures can cause immense pain, reduce mobility, and hinder overall quality of life. The complexity of the disease, with its myriad risk factors ranging from genetics to lifestyle choices, underscores the importance of early detection and prevention. Emphasizing weight-bearing exercises, appropriate calcium and Vitamin D intake, and being judicious with medications that might exacerbate the condition are paramount. Additionally, advanced diagnostic tools like the DEXA scan offer valuable insights into bone density and the severity of osteoporosis. While there’s an array of treatment options, from calcium supplements to bis-phosphonates, prevention remains a cornerstone. As spine health professionals, our role in educating, diagnosing, and guiding patients through this journey is pivotal.
Thank you