Best Spine Surgeon in Mumbai | Dr. Amit Sharma

+91-9967600461
draks777@gmail.com
Understanding Spine MRI: A Patient’s Guide
Understanding Spine MRI: A Patient’s Guide
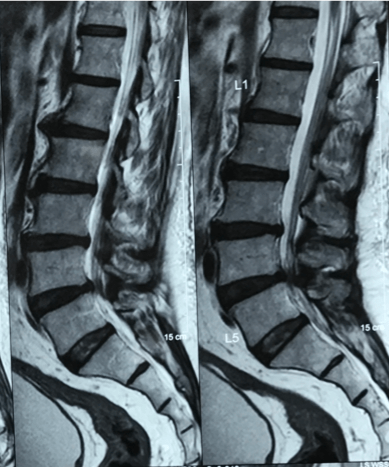
Introduction: MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is a valuable diagnostic tool used by healthcare providers to assess spinal health. Understanding MRI findings empowers patients to engage actively in their healthcare journey. In this guide, we’ll explore common MRI findings, their significance, and how patients can interpret them within the broader context of their health.
- Herniated Discs: A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner core of a spinal disc protrudes through the tough outer layer. This can cause symptoms like back pain, leg pain (sciatica), numbness, or weakness. MRI helps identify herniated discs, guiding treatment decisions.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Degenerative changes in the spine, such as disc degeneration and bone spurs (osteophytes), are common with aging. These changes can lead to symptoms like back pain and reduced mobility. MRI findings help doctors assess the severity of degeneration and plan appropriate interventions.
- Disc Bulge: A disc bulge occurs when the disc’s outer layer extends beyond its normal boundary. While disc bulges are common and may not always cause symptoms, they can contribute to nerve compression and pain. MRI helps evaluate the extent of bulging and its impact on surrounding structures.
- Spinal Stenosis: Spinal stenosis involves the narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramina, leading to nerve compression. MRI is crucial in diagnosing spinal stenosis and guiding treatment decisions, which may include medication, physical therapy, or surgery.
- Spondylolisthesis: Spondylolisthesis occurs when one vertebra slips forward or backward relative to another. MRI helps identify this displacement and assess its impact on nearby structures. Treatment options depend on the severity of symptoms and may include bracing, physical therapy, or surgery.
- Tumors and Infections: MRI is highly sensitive in detecting tumors, infections, or other abnormalities affecting the spine. Timely identification of these conditions is critical for prompt intervention and management. Treatment may involve surgery, chemotherapy, or antibiotics, depending on the nature of the condition.
- Traumatic Injuries: In cases of traumatic injuries, such as fractures or spinal cord injury, MRI provides detailed information about the extent of damage to bones, soft tissues, and nerves. This helps doctors formulate a comprehensive treatment plan, which may include immobilization, surgery, rehabilitation, or pain management.
Interpreting MRI Findings: While patients may attempt to understand MRI reports, it’s essential to recognize that interpreting these findings requires medical expertise. Patients should trust their healthcare provider to correlate MRI findings with their symptoms and clinical history. Not all MRI findings are clinically relevant or the cause of symptoms. It’s crucial to avoid unnecessary worry and leave the interpretation of MRI findings to trained professionals.
Conclusion: MRI findings provide valuable insights into spinal health, guiding treatment decisions and improving patient outcomes. Patients should engage in discussions with their healthcare providers to understand their MRI results fully. Remember, your doctor is best equipped to interpret MRI findings in the context of your overall health and symptoms. Trust in their expertise and collaborate in your journey toward better spinal health.